What Are AI Assistants?

AI assistants help users by completing tasks and answering questions. They aim to make routine tasks easier and improve productivity through guided interactions.
- How They Work: AI assistants rely on natural language understanding (NLU) and pre-programmed responses. They are reactive, meaning they only act when the user instructs, and are primarily task-focused.
- Features of AI Assistants:
- User Interaction: Designed to engage with users through voice or text commands.
- Task Execution: Perform straightforward actions like sending emails, setting reminders, or providing search results.
- Connected Ecosystem: Often integrated into smart devices, allowing seamless control of various tools.
- Real-World Examples:
- Google Assistant: Helps users find directions, control smart home devices, and manage daily schedules. For instance, it can adjust your thermostat or turn off lights with a voice command.
- Amazon Alexa: Powers smart homes by playing music, controlling appliances, and even placing online orders. An example is asking Alexa to reorder household supplies from Amazon.
- Siri (Apple): Acts as a digital personal assistant for iPhone users, helping with tasks like sending messages, making calls, or finding quick answers to questions.
- Practical Use Cases:
- Customer Support: Chatbots powered by AI assistants handle FAQs, reducing wait times for customers.
- Smart Homes: Assistants like Alexa integrate with IoT devices for hands-free control.
- Personal Productivity: Managing calendars, reminders, and email replies.
What Are AI Agents?

AI agents are more advanced systems designed to operate autonomously. Unlike AI assistants, which rely on user input, AI agents act independently to achieve specific goals. They can analyze situations, make decisions, and adapt to changes in their environment without constant human supervision.
- How They Work: AI agents utilize advanced algorithms, including machine learning, reinforcement learning, and predictive analytics. These technologies allow them to perform complex, multi-step tasks, monitor environments, and make decisions in real-time.
- Features of AI Agents:
- Autonomy: Can act without continuous user interaction.
- Goal-Driven Behavior: Focuses on completing objectives rather than individual tasks.
- Adaptability: Learns from experience and refines its actions over time.
- Real-World Examples:
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI agents like those in Tesla cars navigate roads, make driving decisions, and respond to traffic conditions without human input.
- Stock Trading Bots: AI agents in platforms like Robinhood or Alpaca analyze market trends and execute trades automatically to maximize profits.
- Healthcare Diagnostics: AI agents such as IBM Watson analyze patient records, medical images, and research papers to assist in diagnosing illnesses and recommending treatments.
- Practical Use Cases:
- Industrial Automation: AI agents monitor machinery for signs of wear, predict failures, and schedule maintenance to reduce downtime.
- Supply Chain Management: Tools like Blue Yonder’s AI agent optimize inventory, forecast demand, and plan delivery routes.
- Energy Management: AI agents optimize energy usage in buildings by adjusting heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy and weather patterns.
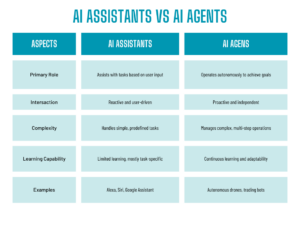
Key Differences Between AI Assistants and AI Agents
When to Use AI Assistants
AI assistants are most effective when the focus is on:
- Personal Tasks: Helping users stay organized or control devices.
- Customer Engagement: Offering quick responses to standard questions.
- Basic Automation: Managing straightforward, repetitive actions.
Example:
A retail business can deploy an AI assistant chatbot to guide customers, answer common queries like “Where is my order?” or “What are your return policies?” and escalate complex issues to human agents.
When to Use AI Agents
AI agents are ideal for scenarios requiring:
- Complex Problem-Solving: Analyzing data and making decisions in dynamic situations.
- Autonomous Operations: Acting without human intervention for extended periods.
- Optimization: Improving efficiency in processes like logistics or production.
Example:
In the logistics industry, an AI agent can monitor real-time delivery routes, adjust for traffic or weather conditions, and reroute deliveries to minimize delays, saving both time and costs.
Challenges and Limitations
Both AI assistants and AI agents come with their challenges:
- AI Assistants:
- Limited to basic tasks and heavily dependent on user commands.
- Cannot adapt to new or unforeseen situations.
- AI Agents:
- Extensive development, testing, and data are required to ensure reliability.
- They can raise ethical concerns if they make decisions with unintended consequences, such as biases in healthcare or finance.
Conclusion
AI assistants and AI agents serve different purposes and solve distinct problems. Assistants focus on enhancing user interactions and simplifying everyday tasks, while agents excel in autonomy, adaptability, and achieving long-term goals. Businesses and individuals can benefit from understanding their capabilities to choose the right solution for their needs.
As technology evolves, the line between AI assistants and agents may blur, with advancements leading to systems that combine the best of both worlds—autonomous yet user-friendly. For now, knowing the difference allows us to unlock the full potential of AI in our lives.

